【Rails】技術面接対策の記事の質問を多少深ぼる記事①
はじめに
こんにちは!大ちゃんの駆け出し技術ブログです。
技術面談の対策としてRUNTEQでは以下の記事をおすすめしています。
53問もありますし充実しています。そして問題を解こうとすると案の定言葉で説明できないことが多かったです。しかし、このサイトの回答自体も意図的か明確に回答を書いていません。所々「この回答で十分なの?」と思うことがありました。そこで何記事かに渡って53問全てを深掘りして回答をここに残したいと思います。就活も進められるし自分の理解も深められるし一石二鳥です!
Q1: ブログアプリで記事のリストを取得するときのリクエスト/レスポンスサイクルをひととおり説明してください
ユーザーが記事のリストを取得するボタンをクリックしたときに/articlesのURLにGETのリクエストを送信します。
その後、routes.rbに割り当てられているそのリクエストに対応するArticlesコントローラーのindexアクションを実行します。
# config/routes.rb Rails.application.routes.draw do get 'articles', to: 'articles#index' end
indexアクション内でArticle.allが実行されて、Articleモデル経由でDBから記事リストのデータを取り出し、インスタンス変数(@articles)に代入されます。
class ArticlesController < ApplicationController def index @articles = Article.all end end
最後にビュー側で記事リストが格納されている@articlesを展開しユーザーに表示します。
<!-- app/views/articles/index.html.erb --> <% @articles.each do |article| %> <tr> <td><%= article.title %></td> <td><%= article.content %></td> </tr> <% end %>
Q2:「Rubyでは(ほぼ)あらゆるものがオブジェクトである」について説明してください
オブジェクト指向言語におけるオブジェクトとはクラスのインスタンスのことを示すらしいです。これについては一応別の記事も参照して確認しました。
オブジェクトを定義する雛形をクラス(class)、クラスに基づいてプログラム実行時にコンピュータのメモリ上に展開されたオブジェクトのことをインスタンス(instance)と言うが、実際上はインスタンスのことを指してオブジェクトと呼ぶことも多い。
↓
Rubyにおけるすべてのクラスは最終的にスーパークラスを持たないBasicObjectクラスを継承していることがコンソールで確認できます。
# 数値 1.class => Integer 1.class.class => Class # 文字列 "a".class => String i"a".class.class => Class "a".class.superclass => Object "a".class.superclass.superclass => BasicObject "a".class.superclass.superclass.superclass => nil
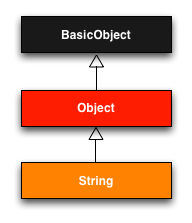
https://railstutorial.jp/chapters/rails-flavored-ruby?version=4.0#sec-a_class_of_our_own
よって、Rubyでは(ほぼ)あらゆるものがオブジェクトであることが言える!となるわけです。
メソッドや条件分のifなどはコンソールで打ち込んでもクラスを継承していないことがわかります。
def destroy logout redirect_to root_path end end => :destroy # destroyメソッドが定義される destroy.class => (irb):37:in `destroy': undefined local variable or method `logout' for main:Object (NameError)
よって"ほぼ"となり全てがオブジェクトというわけではないんですね。
Q3: Rubyの型は静的ですか?動的ですか?
変数の型をいつでも変更できるのが動的型付け言語になります。
a = 2 => 2 a = "a" => "a"
よってRubyは動的型付け言語です。
他の動的型付け言語としては以下が挙げられます。
では静的型付け言語は型を変更できないということになります。正確には変数に代入する前に変数の型を宣言する必要があります。
// Java example int num; // numはIntegerだよと宣言 num = 5; // numにIntegerである5を代入
他の静的型付け言語としては以下が挙げられます。
深くは調べていないのですが、下記記事を参照してそれぞれのメリットデメリットも引用しておきます。
動的型付け言語のメリット
- 記述量が大幅に減る
- 比較的簡単にプログラムが書ける
よって、小規模なシステム開発や小回りが効くアジャイル開発に向いている
動的型付け言語のメリット
- コンパイル時にエラーが出てくれる
- メモリ領域の最適化が行える
よって、大規模なシステム開発などシステム上堅牢性が求められる開発に向いている
Q4: Rubyのゲッターとセッターについて説明してください
この質問が本記事の質問の中で1番難しいと思います。復習の機会になってよかったです。
Rubyではインスタンス変数の値はクラス内からしか取得できないようです。ですので下記のようにクラス外からの呼び出しができていません。
class User def initialize(name) @name = name end end => :initialize user = User.new("a") => #<User:0x00007f837c1118c0 @name="a"> p user.name (irb):13:in `<main>': undefined method `name' for #<User:0x00007f837c1118c0 @name="a"> (NoMethodError)
参照するためにはクラス内にインスタンス変数を参照するメソッド「ゲッター」を定義する必要があります。
class User def initialize(name) @name = name end def getName @name end end => :getName user = User.new("daiki") => #<User:0x00007f837c0a0580 @name="daiki"> p user.getName "daiki" => "daiki"
セッターはインスタンス変数をクラス内で更新するメソッドになります。"="が末尾についたメソッドはセッターメソッドとなります。
class User def initialize(name) @name = name end def getName @name end def changeName=(name) @name = name end end => :changeName= user = User.new("daiki") => #<User:0x00007f837c0e3b00 @name="daiki"> p user.getName "daiki" => "daiki" user.changeName = "dai-chan" # 値を変更 => "dai-chan" p user.getName "dai-chan" => "dai-chan"
Railsを使っていると意識する必要がないところなのですが、理解しておくと応用が効きそうです。とはいうものの使わないから忘れてしまうので、自分は英語の意味で覚えるようにしています。setが少しあやふやですが、、、
get・・・取得する => 値を外部から取得する set・・・設定(定義)する => 値を外部から更新する
アクセスメソッドを使えば簡易的にゲッターとセッターが定義できます。
attr_reader
ゲッターのみ定義
値の更新はできない
class User attr_rader :name #ゲッター def initialize(name) @name = name end end user = User.new("daiki") user.name #=>"daiki"
attr_writer
セッターのみ定義
値の取得ができない
class User attr_writer :name #セッター def initialize(name) @name = name end end user = User.new("daiki") user.name = "dai-chan" #=>"dai-chan"
attr_accessor
ゲッターとセッターどちらも定義できる
class User attr_accessor :name #ゲッターとセッター def initialize(name) @name = name end end user = User.new("daiki") user.name #=>"daiki" user.name = "dai-chan" #=>"dai-chan"
ちなみにRailsではなぜ意識する必要がないのかというと、ActiveRecord::Base を継承したクラスはそのclassが紐づくテーブルのカラムがプロパティ値となり、明示的にgetter or setter を定義する必要がないらしいです。ActiveRecordどんだけ優秀なんだ。
Q5: Rubyであるメソッドを呼び出したときの動作を説明してください
この質問、一見メソッドのことを説明するだけというシンプルな質問に見えますが、よく読むと違います。"動作"を説明する必要があります。
ちなみに質問集のサイトの回答が以下のとおり。
メソッド名を含む1件のメッセージがそのオブジェクトに送信されます。オブジェクトにそのメソッドが存在する場合は、オブジェクトがそのメソッドを呼び出します。以下のようにRubyの
sendメソッドの動作を考えると、この点がよりよく見えてきます。
obj.hello #=> 'hello' obj.send(:hello) #=> 'hello'
?????????????
自分は初見では理解できませんでした、、、、。自分の理解力が低いだけかと、、、、。
sendメソッドがまず分からなかったので調べました。sendメソッドとはレシーバの持っているメソッドを呼び出してくれるメソッドのようです。
class User def name puts "taro" end end user = User.new #定義したメソッドを呼び出す user.name # => taro # sendを使った書き方 user.send(:name) # => taro user.send("name") # => taro
レシーバーであるuserにnameメソッドが定義されているのでそれを引数にしていることでレシーバーの持っているメソッドを呼び出しています。正直どこで使うのか分からないメソッドでしたが、sendメソッドは理解できました。
ここで下記文章を再掲します。
メソッド名を含む1件のメッセージがそのオブジェクトに送信されます。オブジェクトにそのメソッドが存在する場合は、オブジェクトがそのメソッドを呼び出します。
この文章はsendメソッドの流れそのものを表していることが今なら理解できると思います。つまり、sendメソッドを使用するとレシーバーの中に指定したメソッドがあればそのメソッドを呼び出していますね。
- user.send(:name)を実行
↓
- インスタンスであるuserにnameメソッドがあることを確認
↓
- nameメソッドを実行
つまりこれは他のメソッドでも同じように動作しているということが言えます。
- user.nameを実行
↓
- インスタンスであるuserにnameメソッドがあることを確認
↓
- nameメソッドを実行
ということですね。これが普段あまり考えずに使用しているメソッドの動作です。オブジェクトの中に存在すれば実行する。だから、メソッドが存在しなければ存在しなければundefined methodのエラーになる訳ですね。
user.hoge => undefined method `hoge' for #<User:0x00007fb2b48ac668> (NoMethodError)
undefined methodエラーの意味を再確認しました。
Q6: あるRailsアプリ内のルーティングをすべて表示してください
rake routes、もしくはrails routesですね。1番簡単でした。これ本当に質問されるんですかね。
$ rake routes
Prefix Verb URI Pattern Controller#Action
root GET / top#index
login GET /login(.:format) user_sessions#new
POST /login(.:format) user_sessions#create
logout DELETE /logout(.:format) user_sessions#destroy
rails_postmark_inbound_emails POST /rails/action_mailbox/postmark/inbound_emails(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/postmark/inbound_emails#create
rails_relay_inbound_emails POST /rails/action_mailbox/relay/inbound_emails(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/relay/inbound_emails#create
rails_sendgrid_inbound_emails POST /rails/action_mailbox/sendgrid/inbound_emails(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/sendgrid/inbound_emails#create
rails_mandrill_inbound_health_check GET /rails/action_mailbox/mandrill/inbound_emails(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/mandrill/inbound_emails#health_check
rails_mandrill_inbound_emails POST /rails/action_mailbox/mandrill/inbound_emails(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/mandrill/inbound_emails#create
rails_mailgun_inbound_emails POST /rails/action_mailbox/mailgun/inbound_emails/mime(.:format) action_mailbox/ingresses/mailgun/inbound_emails#create
rails_conductor_inbound_emails GET /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#index
POST /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#create
new_rails_conductor_inbound_email GET /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/new(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#new
edit_rails_conductor_inbound_email GET /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/:id/edit(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#edit
rails_conductor_inbound_email GET /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/:id(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#show
PATCH /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/:id(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#update
PUT /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/:id(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#update
DELETE /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/:id(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails#destroy
new_rails_conductor_inbound_email_source GET /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/sources/new(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/sources#new
rails_conductor_inbound_email_sources POST /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/sources(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/inbound_emails/sources#create
rails_conductor_inbound_email_reroute POST /rails/conductor/action_mailbox/:inbound_email_id/reroute(.:format) rails/conductor/action_mailbox/reroutes#create
rails_service_blob GET /rails/active_storage/blobs/redirect/:signed_id/*filename(.:format) active_storage/blobs/redirect#show
rails_service_blob_proxy GET /rails/active_storage/blobs/proxy/:signed_id/*filename(.:format) active_storage/blobs/proxy#show
GET /rails/active_storage/blobs/:signed_id/*filename(.:format) active_storage/blobs/redirect#show
rails_blob_representation GET /rails/active_storage/representations/redirect/:signed_blob_id/:variation_key/*filename(.:format) active_storage/representations/redirect#show
rails_blob_representation_proxy GET /rails/active_storage/representations/proxy/:signed_blob_id/:variation_key/*filename(.:format) active_storage/representations/proxy#show
GET /rails/active_storage/representations/:signed_blob_id/:variation_key/*filename(.:format) active_storage/representations/redirect#show
rails_disk_service GET /rails/active_storage/disk/:encoded_key/*filename(.:format) active_storage/disk#show
update_rails_disk_service PUT /rails/active_storage/disk/:encoded_token(.:format) active_storage/disk#update
rails_direct_uploads POST /rails/active_storage/direct_uploads(.:format)
終わりに
今回はここまで!!!!
次回はQ7からです!